A Guide for Doing Business in Vietnam
Vietnam is a rising star in the global economy, offering a wealth of opportunities and innovation for international investors. With its strong economic growth and political stability, Vietnam has shown remarkable resilience in facing global economic challenges. Vietnam also boasts a rich cultural heritage and a dynamic economic environment, making it an attractive destination for doing business.
In this article, we will examine the reasons why Vietnam appeals to global business players and the various opportunities that the country provides. We will also address some key questions about doing business in Vietnam, the practices and strategies that are essential for succeeding in this vibrant Southeast Asian nation.
Vietnam’s Economic Growth and Global Standing
Vietnam’s Economic Transformation and Growth
Vietnam has experienced a remarkable economic transformation over the last three decades, progressing from a low-income to a lower-middle-income country. Here are the key highlights of Vietnam’s economic journey:
- Rapid GDP Growth: The GDP per capita has increased 3.6 times since the early 2000s, reaching about US$3,700 in 2022. From 2016 to 2019, Vietnam enjoyed an average annual GDP growth rate of 6.7%.
- Resilience Amidst COVID-19: Despite the pandemic, Vietnam’s economy demonstrated remarkable growth, expanding by 8.0% in 2022. The forecast anticipates a moderation to 5.8% in 2023, followed by a pickup to 6.9% in 2024.
- Key Success Factors:
- Embraced trade liberalization and participated in major trade agreements like the ASEAN Free Trade Area, CPTPP, and EU-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement.
- Implemented market-oriented reforms, including deregulation and privatization.
- Attracted significant foreign direct investment, particularly in manufacturing and processing.
- Invested in human capital, enhancing education, healthcare, and workforce skills.
Some of the notable achievements of Vietnam’s economy in the last decade are:
- Vietnam became a lower-middle-income country in 2010, with a GDP per capita of US$1,172.
- Vietnam joined the World Trade Organization in 2007 and became a full member of the ASEAN Economic Community in 2015, integrating more deeply into the regional and global economy.
- Vietnam signed the CPTPP in 2018 and the EVFTA in 2019, two of the world’s most comprehensive and ambitious trade agreements, covering 13.5% and 15.2% of global GDP, respectively.
- Vietnam achieved the Millennium Development Goals ahead of schedule and made significant progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals, especially in reducing poverty, improving health, and promoting gender equality.
- Vietnam successfully contained the COVID-19 pandemic, with relatively low cases and deaths, and facilitating economic recovery with timely and effective fiscal and monetary measures.
Vietnam’s journey reflects its strategic economic policies, global integration, and focus on sustainable development, positioning it as a resilient and growing economy in the region.
Vietnam’s Place in the Global Market
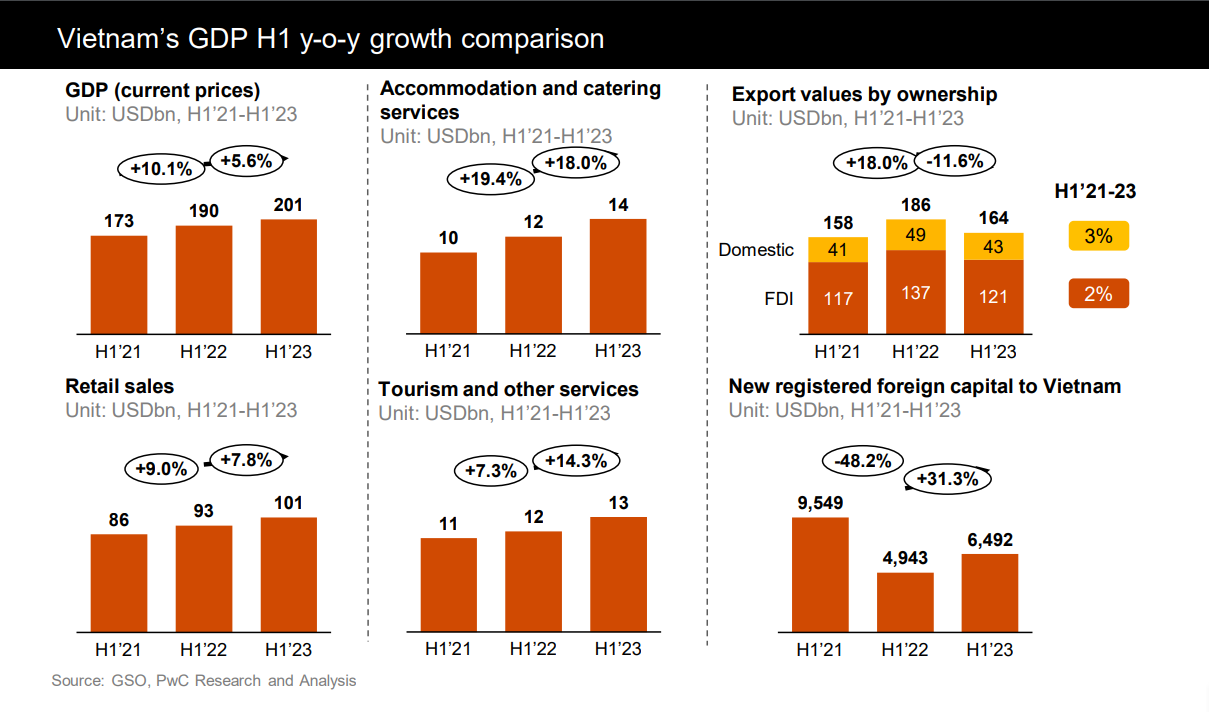
Vietnam is a fast-growing Southeast Asian economy with nearly 100 million people and a US$341 billion GDP in 2022. It has made impressive economic and social progress, reducing poverty and becoming a middle-income country. Vietnam faces many opportunities and challenges in the 21st century as it seeks to maintain its growth, improve its competitiveness, and integrate with the region and the world.
This table shows some key aspects of Vietnam’s economic development and outlook, based on the latest data and analysis:
| Aspect | Summary |
| Trade | Vietnam’s economy is very open and connected to the world, with trade being more than twice as large as its GDP in 2022.
Trades are mostly performed with the US, China, the EU, Japan, and South Korea, and exports and imports a variety of products, such as electronics, textiles and garments, footwear, machinery, agricultural products, raw materials, fuels, and consumer goods. Vietnam recorded a trade surplus of US$15 billion in 2022, indicating that it sold more than it bought. |
| FDI | Vietnam’s economy relies heavily on foreign direct investment (FDI), which accounts for 20% of its GDP, 70% of its exports, and 12% of its employment in 2022.
Most of the FDI comes from Asian countries, especially South Korea, Japan, Singapore, Taiwan, and Hong Kong. The FDI flows mainly to the urban and industrial areas, such as Ho Chi Minh City, Hanoi, Binh Duong, Dong Nai, and Bac Ninh. In 2022, Vietnam attracted US$28.5 billion of FDI inflows and had a total FDI stock of US$220 billion. |
| Digital transformation | Vietnam has embarked on a digital transformation journey, ranking 40th in the Global Innovation Index 2022 and 55th in the Ease of Doing Business 2022.
It has built up its digital infrastructure, such as the 5G network, the national digital identity system, and the e-government platform. It has also fostered the growth of its digital economy, encompassing sectors such as e-commerce, fintech, e-learning, and e-health. |
| Green transition | Vietnam is committed to the green transition and the Paris Agreement on climate change. It has adopted the National Green Growth Strategy 2021-2030, which sets ambitious targets and achievements in various fields, such as:·
|
| Regional integration | Vietnam has deepened its regional integration, joining various regional cooperation mechanisms and initiatives. Some of them are:
Vietnam has enjoyed the benefits of regional integration, accessing larger and more diverse markets, attracting more investment and trade, and enhancing its regional connectivity and infrastructure. Vietnam has also played an active and constructive role in regional integration, contributing to peace, stability, and cooperation in the region. |
| Geopolitical uncertainties | Vietnam’s market is not immune to the geopolitical uncertainties that affect the world, such as the US-China trade war, the COVID-19 pandemic, and the South China Sea disputes.
To cope with these uncertainties, Vietnam has adopted a flexible and pragmatic approach, balancing its relations with the major powers, diversifying its economic partners, and strengthening its domestic capabilities. Vietnam has leveraged the US-China trade war, attracting some of the trade and investment that shifted away from China. Vietnam has also maintained its strategic partnership with the US, expanding its cooperation in trade, security, and defense. Vietnam has also managed its complex and comprehensive relationship with China, promoting its economic cooperation while safeguarding its sovereignty and interests in the South China Sea. |
Ease of Doing Business in Vietnam
Setting up a Business in Vietnam
For entrepreneurs and foreign investors eyeing Vietnam, there are several routes to establish a presence:
- Limited Liability Company (LLC): Ideal for small to medium-sized businesses.
- Representative Office (RO): Suitable for market research and liaison activities.
- Branch Office (BO): A good option for expanding an existing foreign business.
- Joint-stock Company (JSC): Best for larger enterprises with multiple shareholders.
Each of these structures has its unique set of requirements and benefits, catering to different business needs and investment scales.
Tax Advantages for Businesses in Vietnam
Vietnam is a country that welcomes foreign investment with open arms. The Vietnamese government has implemented various tax incentives to attract and support foreign businesses in different sectors. These incentives include:
- Preferential Tax Rates: Lower Corporate Income Tax (CIT) rates for projects in high-tech, education, health care, and environmental protection.
- Tax Holidays and Reductions: CIT exemption for the initial four years, followed by a 50% reduction for the next nine years, and a preferential 10% rate for two additional years for projects in areas with difficult socio-economic conditions or projects with large-scale investment and high-tech application.
- Other Benefits: Import duty exemptions, value-added tax refunds, and personal income tax reductions are available for foreign investors and expatriate employees.
These tax incentives make Vietnam an appealing destination for foreign businesses seeking growth in a supportive fiscal environment.
Opportunities and Industries in Vietnam
Vietnam’s economy is expected to grow by 6.3% in 2023, according to the World Bank, making it one of the fastest-growing economies in the region and the world. The country has successfully contained the COVID-19 pandemic and has implemented various policies to stimulate domestic consumption, attract foreign investment, and promote digital transformation. These factors have created favorable conditions for the development of various sectors and industries in Vietnam, offering opportunities for investors and businesses.

Key Sectors for Investment and Growth
Some of the key sectors that have shown strong potential and performance in Vietnam are:
High-end and Luxury Hospitality
Vietnam has a growing number of luxury hotel properties, with over 150 properties opened in 2022. The hotel market in Vietnam has shown positive performance in both occupancy and revenue per room. Investment opportunities in this sector are backed by a growing tourism industry and the demand for high-end accommodation.
Manufacturing and Logistics
Vietnam’s Manufacturing and Logistics sectors are appealing due to their strategic location, diverse demographics, and favorable trade agreements. The country’s expanding economy, efforts to establish economic zones and industrial parks, and increasing M&A activity are expected to sustain long-term growth in both industries.
Renewable Energy
Vietnam’s renewable energy sector, particularly solar and wind energy, is rapidly expanding, aiming to triple renewable power generation by 2030. The country also relies on hydroelectricity and biomass, with feed-in tariffs and supportive policies driving the growth of renewable energy, especially solar PV. As part of its green energy transition, Vietnam is moving away from coal and increasing the proportion of renewable sources through Power Development Plans.
Retail Banking and Fintech
Retail banking and fintech sectors present opportunities in Vietnam, driven by the underdeveloped banking system and the potential for a cashless society. With substantial room for growth and increasing consumer demand, both banks and fintech firms have attracted significant attention from global investors, with transaction values exceeding US$11 billion in 2022. Key sub-sectors include digital payments, P2P lending, cryptocurrencies, blockchain, investment tech, and point of sales.
E-commerce
E-commerce is thriving in Vietnam despite challenges like growing competition and limited market research due to slow technology adoption. The industry’s strong growth is fueled by progressive government policies, a growing middle-income class, and a fast-expanding Internet economy. The government’s approval of a national e-commerce development master plan further supports digital transformation in the sector.
Regional and Sector-Specific Opportunities
Vietnam’s economic development is not evenly distributed across the country, creating different opportunities and challenges for each region. Some of the regional and sector-specific opportunities are:
Northern Vietnam: Industrial and Technological Hub
Location: Hanoi, Hai Phong, Bac Ninh, Hung Yen, Vinh Phuc.
The northern region stands as Vietnam’s epicenter for industrial and technological advancements. It is a beacon for international corporations looking to tap into the thriving industrial sector.
Key Features:
- Hosts numerous industrial parks, high-tech zones, and innovation centers.
- Attracts FDI from giants like Samsung, LG, Canon, and Panasonic.
- Benefits from proximity to China and access to Hai Phong port.
Primary Sectors: Electronics, automotive, machinery, textiles, footwear.
This region’s industrial growth is bolstered by its strategic location and infrastructure, making it a lucrative choice for businesses in technology and manufacturing.
Southern Vietnam: Tourism, Real Estate, and Financial Services
Location: Ho Chi Minh City, Binh Duong, Dong Nai, Ba Ria-Vung Tau, Long An.
The southern region of Vietnam is the powerhouse of the country’s economy, with a thriving tourism industry in its coastal and delta areas, a booming real estate market, and a sophisticated financial sector.
Key Features:
- Drives over half of Vietnam’s GDP and FDI.
- Known for vibrant tourism in coastal areas and the Mekong Delta.
- Dynamic real estate market and sophisticated financial sector.
Primary Sectors: Tourism, real estate, financial services, retail, logistics.
The region’s economic vitality is enhanced by its cultural and natural attractions, making it a prime location for investors in tourism and real estate.
Central Vietnam: Emerging Markets and Untapped Potential
Location: Da Nang, Quang Nam, Quang Ngai, Binh Dinh, Khanh Hoa.
Central Vietnam, with its emerging markets, offers a blend of untapped potential and rich cultural heritage, presenting diverse opportunities for growth and investment.
Key Features:
- A strategic connector between the north and south.
- Rich in natural and cultural heritage, with sites like Hoi An and Hue.
- Abundant in natural resources and has a skilled workforce.
Primary Sectors: Tourism, renewable energy, mining, oil and gas, agroforestry.
The region’s strategic position and rich resources make it an attractive area for investors looking to explore new markets, particularly in renewable energy and tourism.
Challenges and Risks in the Vietnamese Market
Corruption
Corruption is a major problem in Vietnam that affects many aspects of doing business and undermines the rule of law and public trust. According to Transparency International’s 2021 Corruption Perceptions Index, Vietnam ranked 87th out of 180 countries, indicating a high level of perceived corruption in the public sector.
The government has taken some measures to combat corruption, such as issuing anti-corruption laws and regulations, prosecuting high-ranking officials involved in corruption cases, and enhancing transparency and accountability. However, these efforts have not been sufficient to address the root causes and systemic nature of corruption in Vietnam.
Legal Uncertainty
Legal uncertainty can cause difficulties and risks for foreign investors, such as delays, disputes, and losses. Some of the factors that cause legal uncertainty in Vietnam are:
- Conflicting and overlapping jurisdictions among different government agencies and levels
- Frequent and abrupt changes in laws and regulations, often without proper consultation or notification
- Poor implementation and enforcement of laws and regulations, especially at the local level
- Limited judicial independence and impartiality, as well as low capacity and professionalism of judges and lawyers
- High costs and lengthy procedures for resolving legal disputes, especially through arbitration or litigation
Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) Infringement
Vietnam has a comprehensive legal framework for IPR protection, in line with its commitments under various international agreements, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO), the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP). However, the enforcement of IPR protection remains weak and ineffective due to factors such as:
- Low awareness and respect for IPR among the public and businesses
- Lack of coordination and cooperation among relevant authorities and stakeholders
- Insufficient resources and capacity for IPR enforcement, especially at the border and online
- Low penalties and deterrents for IPR infringement, as well as difficulties in proving and claiming damages
Inadequate Infrastructure
Infrastructure is essential for supporting and facilitating business activities. Inadequate infrastructure can pose challenges and risks for foreign investors, such as:
- High costs and low efficiency of transportation and logistics due to congestion, bottlenecks, and accidents
- Unreliable and insufficient supply of electricity and water, leading to disruptions, shortages, and wastage
- Poor quality and coverage of communication and information technology, limiting access to information and markets
Vietnam has made significant progress in improving its infrastructure in recent years, with the support of the government, the private sector, and international donors. However, the demand for infrastructure still exceeds the supply, especially in urban areas and industrial zones. The main challenges for infrastructure development in Vietnam are:
- Limited public funding and fiscal space due to budget constraints and debt obligations
- Low participation and attractiveness of the private sector due to regulatory barriers, risks, and uncertainties
- Lack of planning and coordination among different sectors and regions, resulting in inefficiencies and imbalances
- Lack of technical and managerial expertise and capacity, as well as transparency and accountability in infrastructure projects
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is vital for ensuring the security, privacy, and integrity of data and information, as well as the continuity and resilience of business operations. Cybersecurity can pose challenges and risks for foreign investors, such as:
- Loss or leakage of confidential or sensitive data and information, such as trade secrets, customer data, and financial records
- Damage or disruption of information systems and networks, affecting business functions and services
- Exposure or vulnerability to cyber threats and attacks, such as malware, phishing, ransomware, and denial-of-service
- Compliance or liability issues due to legal and regulatory requirements, as well as contractual obligations
Vietnam has a high level of internet penetration and digitalization, with more than 70 million internet users and 143 million mobile subscribers. However, the country also faces a high level of cyber threats and attacks, ranking 25th out of 194 countries in terms of the most attacked countries by cybercriminals in 2020.
The government enacted a new law on cybersecurity in 2019, introducing requirements on data localization, business presence, and user information storage, and authentication. The law also mandates that businesses provide information to Vietnamese authorities when requested and prevent and delete certain content within 24 hours. The law has raised concerns among foreign investors, especially in the e-commerce and fintech sectors, regarding its implications for data protection, market access, and freedom of expression.
Conclusion
Vietnam is a dynamic and attractive market in Southeast Asia, with many opportunities for foreign investors and businesses in sectors such as hospitality, manufacturing, renewable energy, fintech, and e-commerce. These sectors are driven by the country’s trade openness, market reforms, foreign investment, and human capital.
However, doing business in Vietnam also faces challenges and risks, such as corruption, legal uncertainty, intellectual property infringement, infrastructure, and cybersecurity. These challenges and risks require foreign investors and businesses to conduct careful research and analysis, seek expert advice and help, and adopt suitable strategies and solutions.
The future of business and investment in Vietnam depends on how the country can overcome its challenges and leverage its opportunities, as well as how it can adapt to the changing global and regional environment. Vietnam has shown its resilience and potential in the past, and it has the ambition and vision to achieve its goals. With the right policies and partnerships, Vietnam can become a leading and sustainable economy in the region and the world.
YOU MAY BE ALSO INTERESTED IN
How To Build Strong Communities Through Events
We live in a time where we are more connected online than ever before. You can send a message to a friend in London while you sit in a coffee shop in Ho Chi Minh City. We have video calls and instant messaging apps that keep us in touch every minute of the day. Yet […]
How to Choose the Right Coworking Membership
Choosing a coworking membership sounds simple until you actually start looking. You realize quickly that “coworking” is a broad term covering everything from coffee shops with fast internet to high-end corporate suites with concierge service. Some spaces feel like vibrant libraries; others feel like networking mixers that happen to have desks. Some are perfect for […]
The Role of Ergonomics in Coworking Spaces
Did you know that the average office worker spends about 1,700 hours a year sitting in front of a computer screen? It is no surprise that many of us go home with stiff necks and aching backs. We often accept this discomfort as a normal part of having a job. We think that tiredness and […]

Interested in this location?
Complete the form below to book a tour or connect with one of our team members to find out more.



