How to Start a Business in Vietnam: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Are you planning to start your own business in Vietnam? If so, you're not alone. Many people aspire to become entrepreneurs but don't know where to start.
- In this article, we'll show you how to start a business in Vietnam from scratch. We'll cover everything from choosing a business idea, registering your company, finding customers, and growing your business.
- By the end of this article, you'll have a clear roadmap for launching and running a successful business in Vietnam. You'll also learn how to avoid the common pitfalls and risks many new entrepreneurs face. Whether you want to start a small or big business, this article is for you. It's packed with practical tips, tools, and resources to help you achieve your goals.
If you are a foreigner who wants to start a business in Vietnam, you might be wondering how to go about it. Vietnam is one of the fastest-growing economies in the world, with many opportunities for entrepreneurs. However, navigating the legal and administrative procedures can also be challenging, especially if you are not familiar with the local language and culture.
In this blog post, we will provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to start a business in Vietnam as a foreigner, covering the following topics:
– The restrictions and conditions for foreign investors
– The common types of business in Vietnam and how to choose the best one for your needs
– The required documents and costs for setting up a company
– The tax matters and obligations for doing business in Vietnam
– The benefits of choosing a coworking space to optimize your costs and network
1. Step-by-Step on How to Start a Business in Vietnam
Step 1: Check the restrictions and conditions for foreign investors
Before starting a business in Vietnam, you must check if your intended business activity is allowed or restricted for foreign investors. According to the Law on Investment (2020), there are some business activities that foreigners cannot carry out in Vietnam, such as:
- Narcotic substances, toxic chemicals, precursors, and minerals
- Natural specimens of endangered, rare, and precious wild fauna and flora species
- Prostitution, human trafficking, or clone of human-related businesses
- Firecracker-related business
- Debt collection
Some business activities are conditional for foreign investors, meaning you must satisfy specific criteria to gain access to the Vietnam market. These include:
- Accounting and auditing services
- Tax agency service
- Customs-related business
- Securities-related business
- Insurance/ Reinsurance/ Insurance brokerage/ Insurance agency/ Insurance auxiliary services
- Price valuation service
- Other financial businesses, such as lotteries, debt collection services, credit rating services, prize-winning electronic games for foreigners, casino business
You can find the complete list of restricted and conditional business activities in the Law on Investment (2020) or consult a professional service provider to help you understand the requirements and procedures.
Step 2: Choose the best type of business in Vietnam for your needs
The next step is to decide what type of business you want to establish in Vietnam. There are two main ways for foreigners to invest in Vietnam: direct and indirect.
Direct investment means you set up a new company in Vietnam, either as a 100% foreign-owned company or a joint venture company with a Vietnamese partner. To do this, you must obtain an enterprise and investment license from the authorities.
Indirect investment means that you buy shares of an existing company in Vietnam. This way, you can have a position in the company management, depending on the agreement between you and the Vietnamese company.
The most common forms of business entities for foreigners in Vietnam are:
- Limited Liability Company (LLC): A company with one or more members liable for its debts only to the extent of its capital contribution. An LLC can be either a single-member LLC or a multiple-member LLC. An LLC is suitable for small and medium-sized businesses that want flexibility and autonomy in management.
- Joint Stock Company (JSC): This company has at least three shareholders liable for its debts only to the extent of their share value. A JSC can issue shares and bonds to raise capital from the public. A JSC is suitable for large-scale businesses that want to access more funding sources and expand their market presence.
- Partnership: This company has at least two partners sharing profits and losses per their agreement. A partnership can be either a general partnership or a limited partnership. A general partnership has unlimited liability for all partners. In contrast, a limited partnership has at least one general partner with total liability and one or more limited partners with limited liability. A partnership is suitable for businesses that want to leverage the skills and expertise of different partners.
- Representative Office (RO): This is not a legal entity but an office representing a foreign company’s interests in Vietnam. An RO can perform non-commercial activities such as market research, promotion, liaison, etc., but cannot conduct direct business transactions or generate income in Vietnam. An RO is suitable for businesses that want to explore the market potential and establish contacts before setting up a full-fledged company.
The choice of the best form of business entity depends on your goals, budget, risk appetite, and industry. Consult with a professional service provider to help you weigh the pros and cons of each option and advise you on the best solution for your needs.
| Business Entity | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Liability Company (LLC) | – Easy to set up
– Flexible management structure – Limited liability protection – No minimum capital requirement |
– Foreign ownership restrictions in certain industries
– Limited ability to raise capital – Potential for disputes among members |
| Joint Stock Company (JSC) | – Ability to raise capital through public offerings
– No foreign ownership restrictions – Limited liability protection |
– More complex and costly to set up than LLC
– Strict regulations on corporate governance – Potential for disputes among shareholders |
| Partnership | – Easy to set up
– Flexible management structure – Shared liability among partners |
– Unlimited liability for general partners
– Limited ability to raise capital – Potential for disputes among partners |
| Representative Office (RO) | – Easy to set up
– Low cost – Allows for market research and promotion |
– Cannot engage in profit-generating activities
– Limited scope of activities – No liability protection |
Step 3: Prepare the required documents and costs for setting up a company
Once you have decided on the form of business entity, you need to prepare the required documents and costs for setting up a company in Vietnam. Depending on the type of business entity, you must prepare specific documents to complete the process of setting up your business in the country. Here are some of the primary documents needed for registering a company in Vietnam:
- Rental contract of registered address of the company
- Charter or articles of association of the company
- List of members or shareholders and their capital contribution
- Passport copies of members or shareholders and legal representative
- Business registration application form
- Investment registration application form (for direct investment)
- Certificate of incorporation or business registration certificate of the foreign company (for indirect investment or RO)
- Power of attorney for legal representative (if applicable)
The costs for setting up a company in Vietnam vary depending on the type of business entity, the capital size, the business activity, and the service provider. Generally, the costs include:
- Market research costs: This is optional but recommended if you want to have a better understanding of the market demand, competition, opportunities, and challenges for your business in Vietnam. The cost of market research depends on the study’s scope, depth, and duration.
- Legal written report: This is optional but recommended if you want to have a clear and comprehensive overview of the legal aspects of starting a business in Vietnam, such as the restrictions, conditions, procedures, and costs. The cost of a legal written report depends on the complexity and length of the information.
- Investment certificate and enterprise certificate costs: These are mandatory for direct investment and vary depending on the type of business entity, the capital size, and the service provider. The average cost ranges from USD 1,250 to 2,500 for foreign-owned enterprises and USD 350 to 1,000 for Vietnamese-owned enterprises.
- Sublicense costs: These are mandatory for some conditional business activities that require additional licenses or permits from the relevant authorities, such as accounting, auditing, tax, customs, securities, insurance, etc. The cost of sublicenses depends on the type and number of licenses or permits required.
- Charter capital: This is mandatory for direct investment and refers to the amount of money the members or shareholders contribute to the company. The minimum charter capital depends on the type of business entity and the business activity. For example, an LLC requires at least VND 10 million (USD 430) as charter capital, while a JSC requires at least VND 30 million (USD 1,300). However, some business activities, such as real estate, banking, education, etc., may require higher charter capital.
- Post-certification procedures: These are mandatory for all business entities and include tasks such as opening a bank account, registering for tax code, printing invoices, applying for social insurance, etc. The cost of post-certification procedures depends on the type and number of tasks required.
You should consult a professional service provider to help prepare the required documents and costs for setting up a company in Vietnam.
Step 4: Deal with tax matters and obligations for doing business in Vietnam
After setting up a company in Vietnam, you need to deal with tax matters and obligations for doing business in Vietnam. You must register for the tax code, file tax returns, pay taxes, and keep accounting records according to Vietnamese tax laws.
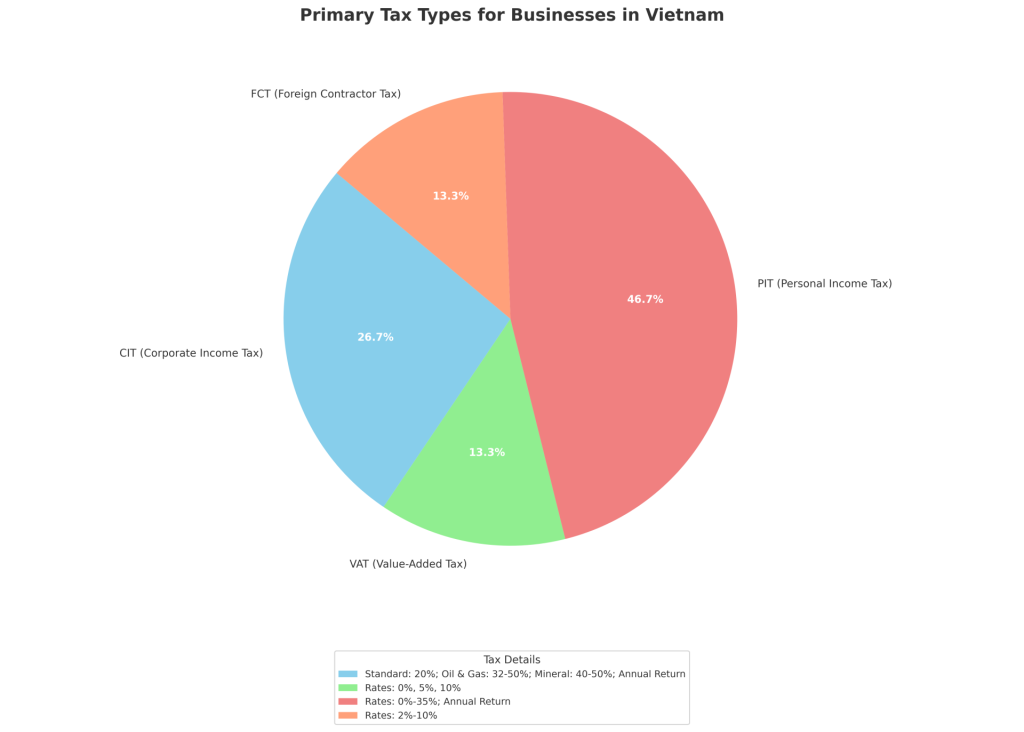
The main types of taxes that you need to pay as a business owner in Vietnam are:
- Corporate income tax (CIT): This is a tax on the profits earned by your company in Vietnam. The standard CIT rate is 20%, but some preferential rates may apply depending on your industry, location, and investment incentives. You need to file CIT returns quarterly and annually and pay CIT accordingly.
- Value-added tax (VAT): This is a tax on the added value of goods and services sold or consumed in Vietnam. The standard VAT rate is 10%, but some reduced rates (5%) or exempted rates (0%) may apply depending on your goods or services. You need to file VAT returns monthly or quarterly and pay VAT accordingly.
- Personal income tax (PIT): This is a tax on the income earned by individuals in Vietnam. The PIT rates range from 5% to 35%, depending on your income level and resident status. You need to file PIT returns annually and pay PIT accordingly.
- Foreign contractor tax (FCT): This is a tax on payments made by Vietnamese entities to foreign contractors for goods or services provided in Vietnam. The FCT rates vary depending on your goods or services and consist of CIT and VAT components. You need to file FCT returns monthly or quarterly and pay FCT accordingly.
- Other taxes: These include taxes such as special consumption tax, natural resources tax, environmental protection tax, import-export tax, property tax, etc., depending on your goods or services.
You should consult a professional service provider to help you deal with tax matters and obligations for doing business in Vietnam.
Step 5: Choose a coworking space to optimize your costs and network
Choosing a coworking space can be an intelligent way to optimize costs when starting a business in Vietnam. Coworking spaces offer flexible and affordable options for entrepreneurs needing a professional and comfortable work environment without renting an office. Coworking spaces also provide opportunities for networking, collaboration, and learning from other like-minded people. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a coworking space for your business in Vietnam:
- Location: You want to choose a convenient coworking space for you and your clients. Consider the accessibility, traffic, parking, and safety of the area. You also want to choose a coworking space that reflects your brand and industry. For example, if you are in the creative field, you might prefer a coworking space that has a vibrant and artistic vibe.
- Amenities: You want to choose a coworking space with the amenities you need to run your business smoothly. These may include high-speed internet, printing and scanning facilities, meeting rooms, coffee and tea, lockers, and mail services. You also want to choose a coworking space with the necessary amenities to enjoy your work-life balance. These may include lounge areas, fitness centers, events, and workshops.
- Cost: You want to choose a coworking space that fits your budget and offers value for money. Compare the prices and benefits of different coworking spaces and see what best suits your needs. Look for discounts, promotions, or referral programs that can help you save money. Remember to factor in the hidden costs such as deposits, utilities, and maintenance fees.
2. Things You Should Prepare Before Starting a Business
2.1. Vision and Idea
Viable business ideas do not have to be revolutionary – they often come from shaking up just one component of existing ideas. Go for numbers, not quality.
To get you started, check out the startup idea matrix for B2C and B2B by the folks at Hackernoon.
Your vision should identify the product or service, the target audience, and the industry.
2.2. Research
Research and testing are the best ways to know if the business idea is good. There are a few ways to go about this.
First, gain a big picture of the industry, competition, and target audience.
- Market research reports
- Trade magazines, news sites, or trade shows
While doing this, you should focus on existing issues, limitations, or new regulations, especially concerning sustainability and safety. These are the gaps that you can fill.
Second, gather opinions on your business idea. You could try:
- Social media surveys.
- Join online forums and communities and present your business idea to your target audience. Ask for their feedback. You can also hold in-person focus groups and interviews.
Third, test-run the idea based on your research. Assemble a limited range of designs, sizes, and versions, or build the prototype. Then, create a website or an online platform featuring the products, do search engine optimization to gauge the market demands for your pilot products, and start learning about your target customers.
2.3. Business Plan
Your first foray into piloting the idea would give you valuable insights into how viable your idea is. Use such insights in building a business plan to turn your idea into a full-fledged startup. You may need to go back to the drawing board to finetune your idea for scaling up, adjusting for operation costs, and looking for financing.
This stage is not linear. It is normal to go back and forth on implementing and refining your idea, sometimes even pivoting towards an adjacent idea or target demographic.
2.4. Financial Essentials
Networking is essential in drawing in funding for your business. Joining local startup communities, attending events, and participating in seminars can open doors to potential investors and partners.
When seeking funding, always ensure that:
- Your business plan is solid and well-researched.
- You understand the terms of any funding agreement, especially if equity is involved.
- Legal agreements are in place, regardless of the funding source.
Here are some good places to start looking for investment.
2.4.1. Bootstrap
Not just your own savings but also the contributions from your immediate family and close friends. It’s the most straightforward way to start. To lower the risk, it is crucial to document any loans or investments from friends and family properly to prevent future conflicts.
2.4.2. Angel investors
Individuals who provide startup capital in exchange for ownership equity or convertible debt. Vietnam has a growing community of angel investors, especially in the tech sector. For example, check out Vietnam Angel Network or this list of top angel investors in Vietnam.
2.4.3. Venture Capital
As Vietnam’s startup scene has grown, so has the interest from venture capitalists (VCs). Local VC firms lead the way in actively investing in Vietnamese startups. Notable VCs include 500 Startups Vietnam, IDG Ventures, and CyberAgent Ventures. Your chosen industry can be a determining factor. For example, SK – a South Korean fund with $2 billion in investment in Vietnam favors consumer and healthcare projects. STIC Investment, which has invested $300 million in Vietnam, is interested in logistics, e-commerce, and healthcare, according to VnExpress.
2.4.4. Incubators and Accelerators
These are organizations designed to help startups succeed. They usually offer office space, mentoring, and sometimes funding in exchange for equity in the company. Examples include the Vietnam-Finland Innovation Partnership Program (IPP) and the Topica Founder Institute.
2.4.5. Government Grants and Competitions
The Vietnamese government, recognizing the potential of startups, occasionally offers grants, competitions, and incentives to promote innovation. For instance, the National Technology Innovation Fund (NATIF) supports tech startups.
2.4.6. Strategic Partnerships
Partnering with established companies in a related field can provide essential funding and expertise. Such partnerships can also give your startup credibility and access to the partner’s customer base or resources.
2.5. Operational Essentials
No matter the type of your business model, here are the basic essentials to take into account:
- Location: remote work or in-person in a home office or coworking space.
- Equipment and tools, either physical or digital.
- Initial inventory and supply chain (if applicable).
- Staffing, salaries, and benefits.
- Branding, marketing, and sales.
- Compliance and reporting
3. The Ultimate Thing You Will Need: Take That Leap of Faith
In 2022, Vietnam became one of the Golden Triangle of Startups in the region, only behind Singapore and Indonesia. The timing is right for anyone who wants to capitalize on the strong growth phase in this country. Would you be one of them? If yes, this is a thriving arena for you.
If you are looking for a place to start a business in Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam, The Sentry is your best choice. We offer flexible solutions for business offices that suit your needs and budget. Our locations are in the most popular and convenient positions in Ho Chi Minh City, close to transportation, shopping, and entertainment.
Whether you need a private office, a coworking space, or a virtual office, we have it all. The Sentry P is located in the heart of District 1, the financial and commercial hub of the city. It has a modern design, high-speed internet, and a friendly staff. The Sentry Z is situated in District 2, the new urban area of the city. It has a spacious layout, natural light, and a cozy atmosphere. Both locations have access to meeting rooms, lounge areas, and coffee bars.
No matter your location, you will enjoy the benefits of being part of The Sentry community. Join us today and take your business to the next level.
YOU MAY BE ALSO INTERESTED IN
How To Build Strong Communities Through Events
We live in a time where we are more connected online than ever before. You can send a message to a friend in London while you sit in a coffee shop in Ho Chi Minh City. We have video calls and instant messaging apps that keep us in touch every minute of the day. Yet […]
How to Choose the Right Coworking Membership
Choosing a coworking membership sounds simple until you actually start looking. You realize quickly that “coworking” is a broad term covering everything from coffee shops with fast internet to high-end corporate suites with concierge service. Some spaces feel like vibrant libraries; others feel like networking mixers that happen to have desks. Some are perfect for […]
The Role of Ergonomics in Coworking Spaces
Did you know that the average office worker spends about 1,700 hours a year sitting in front of a computer screen? It is no surprise that many of us go home with stiff necks and aching backs. We often accept this discomfort as a normal part of having a job. We think that tiredness and […]

Interested in this location?
Complete the form below to book a tour or connect with one of our team members to find out more.



